Bariatrics
Bariatrics
One of the most powerful weight-loss procedures
The biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (or, BPD/DS; or, duodenal switch) is considered one of the most effective operations for weight loss and metabolic syndrome, but patients may experience more frequent nutritional issues.
How the duodenal switch works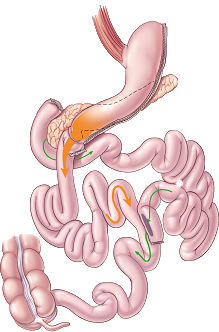
The first portion of the small intestine is divided just past the outlet of the stomach.
A segment of the last portion is then brought up and connected to the outlet of the newly-created stomach so that when the patient eats, the food goes through the newly-created tubular stomach pouch and empties directly into the last segment of the small intestine.
The bypassed small intestine is reconnected to the last portion of the small intestine so that food consumed can eventually mix with your food stream.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Is the duodenal switch right for you?
Patients who undergo the duodenal switch procedure typically experience the following advantages:
Sustained greater weight-loss than gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy
Ability to eat nearly "normal-sized" portions and meals
Favorable changes in gut hormones that reduce appetite, suppress hunger and improve feelings of fullness
Greater control on type 2 diabetes, compared to gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy
Please note that each surgical case is different; advantages may vary based on the specific patient.
The following disadvantages are associated with the duodenal switch:
Higher operative risks than gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy
Hospital stay and recovery time may be longer than other procedures
May cause more bowel gas and bowel movements than other procedures
Patients must adhere to strict dietary and vitamin supplementation guidelines to avoid possible malnutrition
Please note that each surgical case is different. Some patients may not experience any of the disadvantages listed. Final surgical outcomes may vary based on the specific patient.
Office hours
Monday-Friday | 7 a.m. to 7:30 p.m.
Saturday | 9 a.m. to 5:30 p.m.
Address
Fresno Heart & Surgical Hospital
15 East Audubon Drive
Fresno, CA 93720
Get More Information
We use cookies and other tools to optimize and enhance your experience on our website. View our Privacy Policy.